Secure Messaging & Video Conferencing for Healthcare Providers
TrueConf provides secure, HIPAA-compliant messaging and video conferencing that seamlessly connects healthcare professionals with their patients and colleagues.
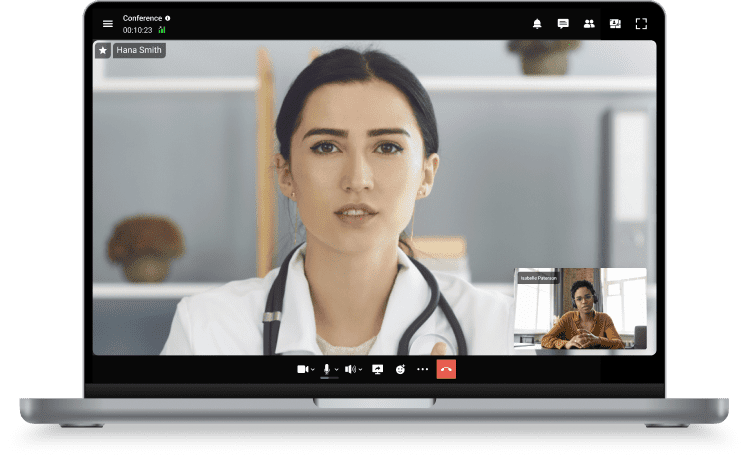
TrueConf provides secure, HIPAA-compliant messaging and video conferencing that seamlessly connects healthcare professionals with their patients and colleagues.
Provide patients with secure, high-quality video consultations, instant messaging with their physician, and browser-based access from any device.
TrueConf empowers healthcare organizations with a unified, secure platform for video conferencing, messaging, webinars, and seamless medical device integration. Built for enterprise-scale environments, it ensures compliance with HIPAA, GDPR, and ISO 27001 while giving hospitals and healthcare systems complete control over sensitive data through flexible on-premises or hybrid deployments.
GDPR Compliant
HIPAA Ready
ISO 27001 Certified
Gain full control over your communications by deploying TrueConf solutions in your enterprise local or virtual network. With TrueConf you can go completely offline and run video sessions without Internet connection. TrueConf features several protection levels, GDPR and HIPAA compliance, which is crucial for clinical services delivered to patients.
Boost collaboration and speed up critical decisions with dedicated channels for departments, teams, or specific medical cases. Empower healthcare professionals to discuss treatment plans, share diagnostic data, and coordinate patient care seamlessly across every unit — from radiology and neurology to intensive care.
Enjoy uninterrupted platform performance with our technical support! From deployment to troubleshooting, our experts provide reliable, accessible, and convenient assistance for professionals.
TrueConf Kiosk
Integrate video conferencing into your interactive system or video kiosk to ensure safe working conditions for medical staff and help prevent the spread of infectious diseases between departments.
TrueConf Server API
TrueConf API unlocks powerful opportunities to integrate video conferencing into third-party telemedicine platforms, online services, and digital products.
TrueConf SDK
With TrueConf SDK, you can bring any telemedicine project to life! Embed video conferencing into your mobile or desktop apps, or develop a fully customized solution for remote healthcare services.
Universitätsklinikum Bonn
Strahlentherapie Bonn-Rhein-Sieg
Sellhorn Ingenieurgesellshaft GmbH
Seniorenheim am Saaleufer GmbH
Krankenhaus GmbH Landkreis Weilheim Schongau
Wenoba
Hospital de Bellvitget
BioCubaFarma

Kennebec Behavioral Health
MIMS Hospital
St Christopher’s Hospice
Maccabi Israel
Campolongo Hospital
Cherokee Indian Hospital
Movendo Technology
Lifewell
FiggHealth
Klinikum Würzburg Mitte gGmbH
Cancer Treatment and Research Center
Sturdy Memorial Hospital
Ostalb Hospital
Bongolo Hospital
In short, HIPAA compliance (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) means meeting strict security and privacy standards for any software used to store or transmit data related to patients’ personal health information. This applies to protected health information (PHI) transmitted via video, audio or text.
These security and privacy rules are important because patient data and medical records are very sensitive, and this information can be used to harm people, for example, for stealing identity. In parallel, healthcare app development is becoming increasingly vital, offering a comprehensive digital solution that integrates seamlessly with these video conferencing tools to enhance patient care and data management. Thus, these regulations are established to protect remote patient-doctor communication from civil and even criminal punishments for ignoring them.
End-to-End Encryption
This guarantees that transmitted content—video, voice, text, and transferred documents—is secured from origin to recipient, minimizing unlawful exposure. Even the platform operator cannot retrieve the contents of sensitive conversations. Such encryption remains essential for ensuring patient privacy within clinical workflows.
Business Associate Agreement (BAA)
A BAA represents an official agreement linking a healthcare entity with the conferencing solution provider, mandated under HIPAA regulations. It specifies where personal health information (PHI) is processed and preserved. Without an executed BAA, a system fails to meet HIPAA standards.
Access Controls & Authentication
HIPAA-ready services apply firm identity validation, integrating distinct login details and protected credentials. Privilege-based permission guarantees only verified individuals may retrieve or alter confidential records. This stops improper actors from intruding into patient-related datasets.
Audit Logs
Platforms are expected to retain comprehensive logs for user sessions, covering who accessed content, when, and specific system activities. These trails are critical for policy enforcement and threat detection. They enable health entities to retain traceability and identify misuse efficiently.
Secure Data Storage
When sessions get saved or files exchanged, they require archiving in encrypted, HIPAA-approved repositories. These solutions must feature defensive mechanisms to deny unauthorized interaction or modification. This setup safeguards PHI both during and after digital engagements.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA introduces an added checkpoint for verifying identity, beyond usernames and passwords alone. It may utilize a device-generated code, fingerprint, or facial scan to complete access. Such defenses reduce vulnerability even when credentials are exposed.
Secure Screen & File Sharing
Compliant conferencing tools permit screen viewing and document exchange under encrypted transmission layers. These functions come regulated to confirm PHI is shielded in collaborative situations. The approach proves vital in virtual care sessions and interdepartmental coordination involving sensitive files.
TrueConf
TrueConf offers a 4K telemedicine platform that works offline, without Internet connection, and can be hosted on your hospital’s premises. It delivers reliable communication experience and protects sensitive health data, integrates with medical equipment, supports DICOM file and test results sharing, video capturing from various equipment (e.g., endoscopes), patient monitoring and live surgical streaming.
TrueConf can be used on all popular operating systems and browsers, allowing patients and doctors to connect from their own devices. Additionally, it can be embedded to existing apps and solutions, e.g. telehealth apps.
Key features:
• TrueConf offers a free version for up to 50 participants with no time limits
• Secure video chats and conferences with a number of collaboration tools
• Self-hosted and works offline
• Client applications for all popular platforms
• TrueConf API opens up new opportunities for the integration video conferencing into third-party telemedicine systems.
Doxy.me
Originally created for university research, Doxy.me provides remote medical care via video and audio. As one of the most popular communication solutions, Doxy is a HIPAA-compliant video conferencing tool. The program’s interface is user-friendly, patients don’t need to install or log in to connect and communicate with healthcare providers.
Doxy’s waiting room feature includes a patient queue and allows patients to check in virtually, so their provider knows they’re ready for the appointment. Each waiting room is customizable with images, videos, and reading materials for patients. In-app appointment management offers higher levels of flexibility compared to other video conferencing services. Providers can reschedule appointments quickly if a patient is running late.
Key features:
• Free for limited services, $35 per month for individual professionals, $50 per user for clinics
• Reviewers on Capterra highlighted the solution’s free option and ease of use but mentioned that calls drop if the internet service isn’t strong
• Mobile notifications make it easy for patients to receive messages.
Thera-LINK
Like Doxy.me, Thera-LINK is a browser-based video conferencing tool focused on mental and behavioral health providers. HIPAA and HITECH compliant, all web traffic, video, database, and file backup within the tool is encrypted. Couple, family, and group sessions are possible by allowing multiple participants in a meeting.
Although it does not come with a free plan, Thera-LINK is provided with scheduling features and bandwidth auto-detection to ensure the right video quality is selected automatically without any user input.
Key features:
• Individual plans: $30 per month (limited to five sessions per month), $45 (unlimited sessions), $65 (unlimited sessions and other security benefits)
• Focused on mental and behavioral health
• Practice management (PM) for individuals and small to medium-sized organizations.
TheraNest
TheraNest is a web-based mental health solution used by individual, group, nonprofit, and educational organizations. Providers can use these tools for video conferencing sessions with a maximum of six participants per session. Other features include insurance billing workflows, calendar scheduling and unlimited storage of client information. Telehealth tools allow clients to join sessions via personalized session links without having to enter a password or download software.
Key features:
• $38 per month (additional $10 for each user to take advantage of HIPAA-compliant video conferencing)
• Unlimited users and storage
• Specifically tailored for mental health applications.
SimplePractice
SimplePractice Telehealth is a HITRUST and HIPAA-compliant telehealth application that allows providers and patients to connect via secure video communication for virtual consultations.
Its software is well designed, and flows more intuitively than many other products on the market. SimplePractice includes not only basic teleconferencing tools, but also online booking, file sharing and auto-payment for credit card billing. Patients can make their own appointments through an in-app calendar and share information before appointments.
SimplePractice also offers an impressive variety of options for plans & notes – Wiley Planners, pre-built templates for numerous professions, and a tool to create forms from scratch.
Key features:
• Individual plans: $39 per month for Essential plan, $59 per month for Professional plan (includes several extra features such as HIPAA-compliant messaging)
• Group plans: $59 per month for the first clinician, $39 for each additional clinician
• Includes integrated features such as free appointment reminders (SMS, email, and voice), a mobile app, and e-claim filing.
Zoom for healthcare
Zoom is known for its free cloud-based video conferencing capabilities, but it also offers a HIPAA-compliant health care plan. The service offers in-app file sharing, a patient waiting room, mute/unmute audio features, screen sharing and desktop recording, a chat messenger, a whiteboard tool and AES 256 encryption.
Zoom for Healthcare doesn’t offer important services like billing or appointment scheduling features. However, it does offer the ability to integrate with third-party applications through dedicated healthcare software services.
Key features:
• $200 per month for up to 10 accounts
• Consistent, high-quality video
• Commonly used for webinars.
VSee
VSee is a secure telemedicine platform with a variety of HIPAA-compliant solutions. Patients can send status updates such as photos, food diaries and mood charts.
The free plan includes unlimited one-on-one video calls both through the app and browser, unlimited secure messaging, real-time annotation screen sharing and file transfers using end-to-end encryption.
VSee Clinic can also be used to simplify patient care with efficient workflows that free up time for both providers and patients.
Key features:
• $49 per month for individual users; contact sales for enterprise pricing
• Used by large organizations, such as Shell and NASA
• Optimized for areas of poor internet service so it’s good for clients overseas or in rural areas.
GoToMeeting
Although GoToMeeting does not have a specific medical focus for video conferencing, the software is HIPAA compliant. For telemedicine, GoToMeeting offers high-quality video, enhanced audio, encrypted sessions, in-app note taking, screen sharing, appointment blocking, and chat messaging, allowing healthcare providers to communicate securely and efficiently with their patients from anywhere.
While GoToMeeting is sufficient for video conferencing, it lacks patient management tools such as medical device integration, billing or appointment scheduling.
Key features:
• $12 per month for Professional plan with limited meeting organizers
• For Enterprise plans, contact sales
• Suitable for many different device types.
Medici
Medici is a mobile telemedicine app that provides virtual care via high-quality video and secure text messaging. Patients can view a physician’s pre-treatment consultation course and request video calls at any time.
Medici provides not only HIPAA-compliant chat and video calling software, but also other features such as real-time translation for more than 20 languages, built-in revenue dashboards, multi-patient and clinical workflow management systems.
Key features:
• Medici offers both a free and paid plan that starts from $149.00 per month, per provider
• A robust mobile app gives doctors access to almost every feature on the go
• Patients easily get messages through mobile notifications.
Mend
Mend is a cloud-based healthcare communication solution that enables patients and providers to connect and share files, messages, assessments, photos and data.
Mend provides options for integrating telemedicine software with electronic medical records. Users can share information with patients or within the organization using a drag-and-drop interface to upload files and invite patients to chat using email links.
Mend can also be used to collect health information from patients like consent forms, medical histories, scanned images of identification, case management documentation and more.
Key features:
• Individual plans: $49 per month (if paid annually)
• Seven-day free trial
• Patient intake forms and appointment reminders are available for all plans
• No download needed.
Chiron Health
Healthcare providers can take advantage of Chiron Health’s cloud-based video meeting services. This HIPAA-compliant tool offers EMR systems integration and streamlines workflow management, insurance verification and billing. Appointment calendars show physician availability and allow patients to schedule appointments.
Automated appointment reminders inform patients of upcoming appointments. The solution is able to automatically calculate patient payments such as co-pay and co-insurance.
Key features:
• Independent plan: $150 per month, per provider ($1,440 when billed annually)
• Guarantees full reimbursement through private payers
• Unlimited live video visits, scheduling, automated appointment reminders, branded web app and email communications, and patient mobile apps available for all plans
• Integrates with EHR/PM tools.
VTConnect
VTConnect offers a HIPAA and HITECH-compliant telemedicine solution to connect securely with clients from virtually anywhere, anytime using any device. Video conferencing technology enables not only individual sessions but also group sessions, allowing patients and providers to connect to the system via desktop and mobile devices.
VTConnect allows its users to enjoy features such as live chat, file sharing and data storage. End-to-end encryption and password protection are used to ensure the safety of PHI.
Key features:
• Provides HIPAA Compliant legal and consent form templates starting from $45
• Individual plans : $49.95 per month with unlimited teleconferencing and signed BAA
• Professional plans : $199.95 per month (includes up to 5 practitioner license, unlimited teleconferencing and signed BAA)
• Virtual Online Office Portal for collecting payments, encrypted messaging, sharing documents and more.
MegaMeeting
MegaMeeting is a robust, all-in-one solution for telemedicine services. For users, it is a platform that provides video conferencing and webinars in a single, user-friendly interface. Collaboration tools work seamlessly thanks to powerful communication features. Doctors can share their screens, share files and chat with patients. Unique access keys ensure the highest level of HIPAA-compliant security.
Additionally, each provider can integrate MegaMeeting telemedicine solutions with their existing health record systems and electronic scheduling.
Key features:
• Plans start at $19 per month, per host when billed annually (for up to 20 attendees per meeting)
• 14-day free trial option before purchase
• Allows for private branding for more a professional look, as well as branded URLs through a custom DNS feature
• Meetings are recorded as .mp4 files.
eVisit
The eVisit platform supports telehealth services for small and large medical providers, including private practices, hospitals, clinics, and health systems. eVisit also includes EMR integrations, scheduling and waiting room management, follow-ups on discharged hospital patients, scheduling on-demand appointments, managing prescriptions, all the way up to billing and payments, using payment links. Providers receive updates and notifications about patient wait times. Flexible scheduling enables both walk-in visits with on-call providers and appointment booking for telemedicine services.
Key features:
• eVisit doesn’t offer a free trial or free version of the software
• Request a demo for pricing information
• All eVisit users have access to unlimited technical support.
Webex for Healthcare
WebEx has described its WebEx for Healthcare video conferencing and mobile app as easy to use and easy to host. With WebEx, a provider has the ability to conduct remote video consults with patients, and message patients with quick answers to questions. Patients can book their own appointments through the calendar functionality within the app.
Webex is also ideal for group practices or organizations because you can use it to send documents to other providers, host team meetings, or training sessions, while still keeping client and organization information secure.
Key features:
• Plans start at $13.50 per month, per host
• Customer support at any time
• A wide range of collaboration tools.
WhatsApp and FaceTime are widely used communication apps that support text, voice, and video calls. While their popularity makes them convenient options, they are not automatically suitable for use in the healthcare industry, where transmitting protected health information (PHI) requires strict HIPAA compliance. To meet HIPAA standards, any platform handling PHI must sign a Business Associate Agreement (BAA) with the healthcare provider and implement specific security measures.
Although both apps offer end-to-end encryption, they lack essential access controls and do not support BAAs. This makes them unsuitable for healthcare use under HIPAA regulations. As a result, despite their strong encryption, WhatsApp and FaceTime are not considered HIPAA compliant due to these security and legal limitations.